Welcome to Neouchiha’s Blog
Feel Free to Look at my CTF_Writeups and other Projects.
Cotopaxi Guide
A guide on how IoT protocols work and how to use cotopaxi
Date:25-5-23
Time:09:07
New protocols like CoAP, DTLS, and MQTT were introduced and old ones like UPnP and SSDP were removed.
CoAP :
Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) is a specialized web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and constrained networks in the Internet of Things. CoAP is designed to enable simple, constrained devices to join the IoT even through constrained networks with low bandwidth and low availability.
This is CoAP message format :
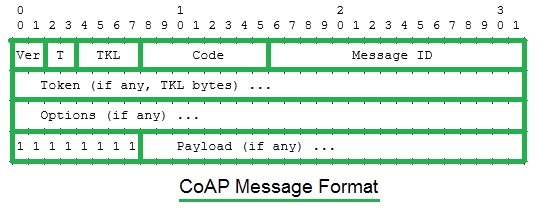
DTLS :
DTLS stands for Datagram Transport Layer Security. It’s a session layer communications protocol designed to protect data privacy. It allows datagram-based applications to communicate while preventing tampering, eavesdropping, and message forgery. Although DTLS is based on TLS, they are two different things. Whereas DTLS is built on UDP, TLS uses Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
MQTT :
MQTT is a standards-based messaging protocol, or set of rules, used for machine-to-machine communication. Smart sensors, wearables, and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices typically have to transmit and receive data over a resource-constrained network with limited bandwidth. These IoT devices use MQTT for data transmission, as it is easy to implement and can communicate IoT data efficiently. MQTT supports messaging between devices to the cloud and the cloud to the device.
MQTT-SN is MQTT Sensor Network protocol Its a UDP based clone of MQTT Minor changes in packet formats
QUIC :
Quick UDP Internet Connections Created by Google and widely used by Google apps and its UDP based
These protocols were not tested by security testing tools.

This is where cotopaxi comes into play. This Tool has multiple purposes like Find active endpoints Identify network traffic fuzz components or interfaces test traffic amplification
The Toolkits in cotopaxi
Reconnaissance Phase :
Service Ping :
Checking the availability of network services Identifies active service endpoints Better than standard tools because nmap and wireshark do not recognize IoT traffic on nonstandard ports
Security Scanner :
Verifying security settings (cipher suites and certificates)
Software fingerprinting :
The software used by the remote network server Equvalent to nmap -sV Uses machine learning classifier
Resource Listing (dirbusting) :
Discovering resources identified by the given URLs Equivalent to Dirbuster for CoAP/mDNS/SSDP Has a list of URIs or services
Device Identification :
Passive analysis of traffic and device classification using Machine Learning Identification of IoT devices using captured traffic (PCAP format)
Pre-Exploitatio Phase :
Amplification sniffing :
Detecting network traffic amplification Calculates amplification factor (size out / size in -1) should be placed on the router or use network tap to see all traffic to/from the target
Protocol Fuzzing :
Fuzzing implementation of protocols checks service ping before and after sending the payload in verbose mode displays payload and response packet.
Vulnerability testing :
Identifying known vulnerabilities 5 classes information disclosure: unauthorized access to internal information crash (DoS) : leads to crash of the server traffic amplification: responses larger than the request memory leak: server wastes memory after processing the payload so it requires manual confirmation remote code execution: currently only detected as crash
Installation
pip install cotopaxi
or install from source
git clone https://github.com/Samsung/cotopaxi
cd cotopaxi
python setup.py install
Usage
Start the services by opening separately.
python -m cotopaxi.service_ping -h
python -m cotopaxi.resource_listing -h
python -m cotopaxi.protocol_fuzzer [IP] PORT -P DTLS
python -m cotopaxi.vulnerability_tester [IP] -P DTLS